
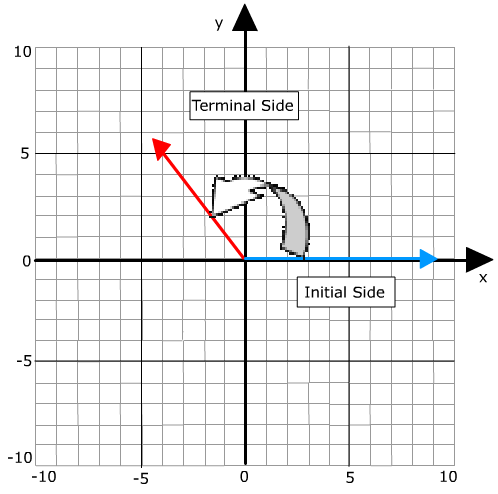
The one on the left goes counterclockwise and is defined to be a positive angle. Notice that there are little curved arrows in the above drawing. When an angle is drawn in standard position, it has a direction. Two angles in standard position are shown below. The Greek letter theta ( ) is often used to represent an angle measure. This positioning of an angle is called standard position. The other ray is called the terminal side of the angle. This ray is called the initial side of the angle. The vertex is always placed at the origin and one ray is always placed on the positive x-axis. In trigonometry, angles are placed on coordinate axes. The rays meet at a point called a vertex. These new functions can be used in many situations that have nothing to do with triangles at all.īefore looking at the new definitions, you need to become familiar with the standard way that mathematicians draw and label angles.įrom geometry, you know that an angle is formed by two rays. One use for these new functions is that they can be used to find unknown side lengths and angle measures in any kind of triangle.

In a right triangle you can only have acute angles, but you will see the definition extended to include other angles. The new functions will have the same values as the original functions when the input is an acute angle.
You will now learn new definitions for these functions in which the domain is the set of all angles. The domain, or set of input values, of these functions is the set of angles between 0° and 90°. For example, the six trigonometric functions were originally defined in terms of right triangles because that was useful in solving real-world problems that involved right triangles, such as finding angles of elevation. Mathematicians create definitions because they have a use in solving certain kinds of problems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
